There are three macronutrients in nutrition – protein, fat, and carbohydrates. Proteins are the structural components of organs, soft tissues, muscle fibers, skin, hair, nails, and blood. They can function as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies. Proteins are used to transmit and store molecules throughout the body. Excess protein that surpasses the need for muscle tissue maintenance is used for energy.

Protein Requirements
Adult Dogs
20g minimum allowance
25g recommended allowance
Puppies
35g minimum allowance
43.8g recommended allowance
Adult Cats
40g minimum allowance
50g recommended allowance
Kittens
45g minimum allowance
56.3g recommended allowance
Essential Amino Acids
Protein digestion begins in the stomach by the enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid. The partially digested food is then transferred to the small intestine. Pancreatic enzymes are released in the small intestine to digest the proteins into amino acids to allow for absorption. Once amino acids are absorbed into the body, they are utilized to create tissue proteins, enzymes, albumin, hormones, and other nitrogen-containing compounds. Excess of amino acids is used for deamination and energy.
Out of the 21 available amino acids in food, there are multiple amino acids classified as essential for dogs and cats. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body in sufficient amounts and must be provided in the diet. The remaining amino acids are non-essential because they can be synthesized by the body if adequate nitrogen and energy are available in the diet.
There are 10 essential amino acids for canines and 11 essential amino acids for felines. Below is a list of essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body in sufficient amounts and must be supplied in the diet.
Requirements for Dogs
- Arginine
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Requirements for Cats
- Arginine
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Taurine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Conditionally Essential Amino Acids
In addition to essential amino acids, there are conditionally essential amino acids the body requires in times of physiologic and pathologic conditions. Particular breeds have inherent predispositions which affect the outcome of synthesized amino acids. Additionally, certain medical conditions can have the same effect on amino acid synthesization.
Glutamine
Physiological factors such as growth, pregnancy, and lactation affect glutamine requirements. Additionally, medical conditions and low protein diets also have an effect on glutamine levels. Critically ill patients have a higher requirement for glutamine. It is suggested that in high times of stress, the body is unable to synthesize sufficient amounts of this amino acid.
Glutamine is conditionally essential and proves beneficial in times of medical conditions such as leaky gut syndrome. Dogs and cats who have digestion issues or leaky gut syndrome benefit from the addition of glutamine-rich foods.
Taurine
Taurine is not considered an essential dietary amino acid for dogs. Unlike cats, dogs are able to synthesize sufficient taurine when the sulfur amino acid precursors, methionine and/or cysteine, are present in adequate amounts in the diet. However, there are medical conditions that increase the need for the amino acid taurine.
Dogs with heart conditions have higher requirements for taurine. In recent developments, taurine deficiency has been linked with the heart condition Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Additionally, there are certain dog breeds who have a genetic predisposition to heart conditions. It is recommended to ensure adequate taurine intake is met for dogs who have heart conditions or a breed known for genetic heart conditions.
Taurine is an essential amino acid for cats because they cannot synthesize their own with other amino acids. Therefore, taurine must be supplied in adequate amounts in the diet.
Food Sources for Amino Acids
Protein quality is determined by the efficiency of amino acid conversion to body tissue. The efficiency of amino acid conversion is dependent on the protein source, the concentration of essential amino acids, and the availability of the nutrients. Proteins that provide optimal amounts of all essential amino acids are classified as complete proteins or high-quality proteins.
High-quality proteins with the most abundant sources of essential amino acids are animal products such as muscle meat, raw meaty bones, and organs. Beef, lamb, pork, turkey, chicken, eggs, and fish are a few examples of animal proteins that all provide all essential amino acids to create a complete diet. The number of amino acids present in each product will depend on multiple factors including animal type, fat content, the diet the animal was fed, processing conditions, storage conditions, and time in storage.
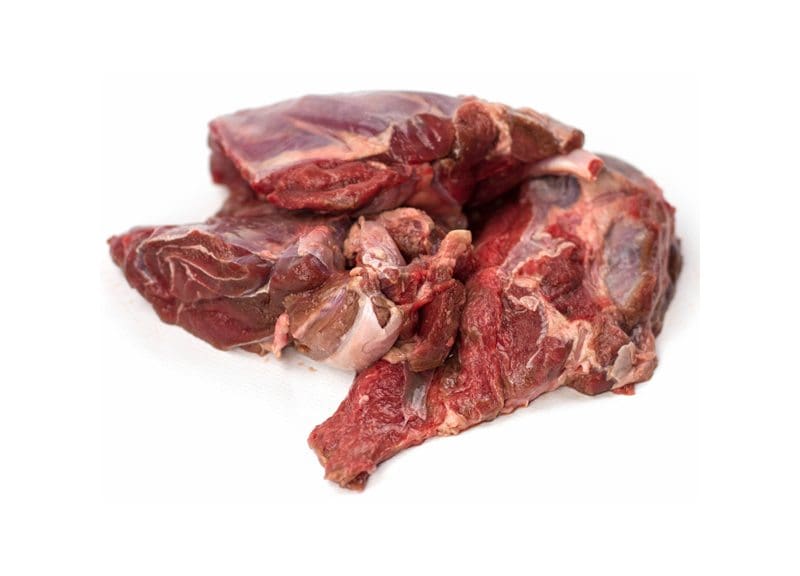

Muscle Meat
Overall muscle meat is abundant in essential and conditional amino acids and should be the main ingredient for raw diets.
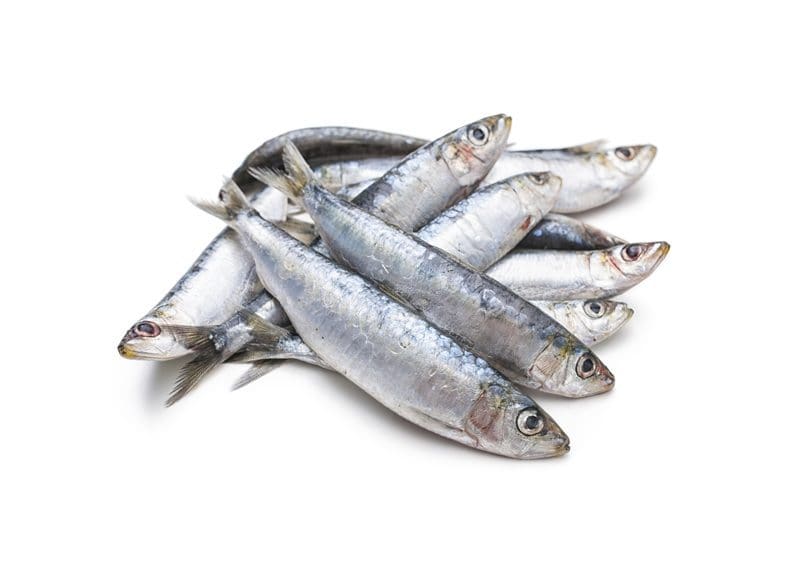

Oily Fish
Oily fish contains high levels of essential and conditionally essential amino acids in addition to their fatty acid benefits.
Conditionally essential amino acids are present in many animal-based ingredients. Nutritional requirements for Glutamine and Taurine are easily obtained when meat, eggs, and fish are fed.
Heart
Harder working muscles will contain higher levels of Taurine. Therefore, heart is a rich source of Taurine.
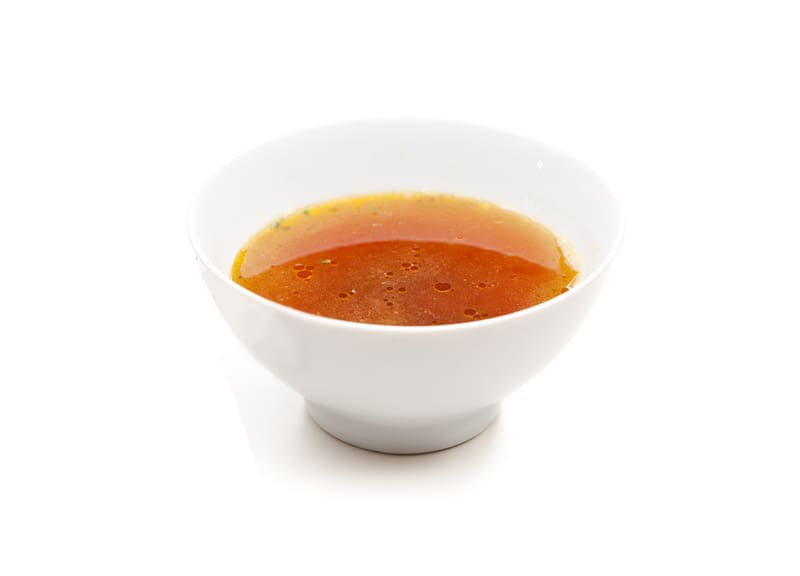

Bone Broth
In addition to muscle meat, bone broth is another rich source of conditionally essential Glutamine.
Proteins with a limited number of essential amino acids are classified as incomplete proteins or low-quality proteins. Plant proteins are incomplete proteins and generally have a lower digestibility than animal proteins. Protein sources can be combined based on their amino acid excess and deficiencies. The combination of multiple protein sources used to improve the overall quality amino acids found in the diet is called protein completion.
Raw diets provide sufficient amounts of amino acids when the diet is created with animal products. This does not mean the diet needs to be entirely composed of animal proteins, but it should be the main component of the diet to provide recommended allowances of essential amino acids in highly bioavailable food sources.
CLOSING COMMENTS
A diet composed of 70% to 80% animal protein, a minimum of 50% being red meat sources, typically exceeds minimum amino acid requirements for dogs. Cats have higher requirements in comparison to dogs. Therefore, they require a diet primarily of animal protein to meet their recommended amino acid requirements.
Raw diets such as PMR for dogs, BARF for dogs, and PMR for cats easily meet protein requirements without adjustments. However, the amount of each amino acid an individual pet requires is dependent on multiple factors including growth, pregnancy, lactation, and medical conditions.
